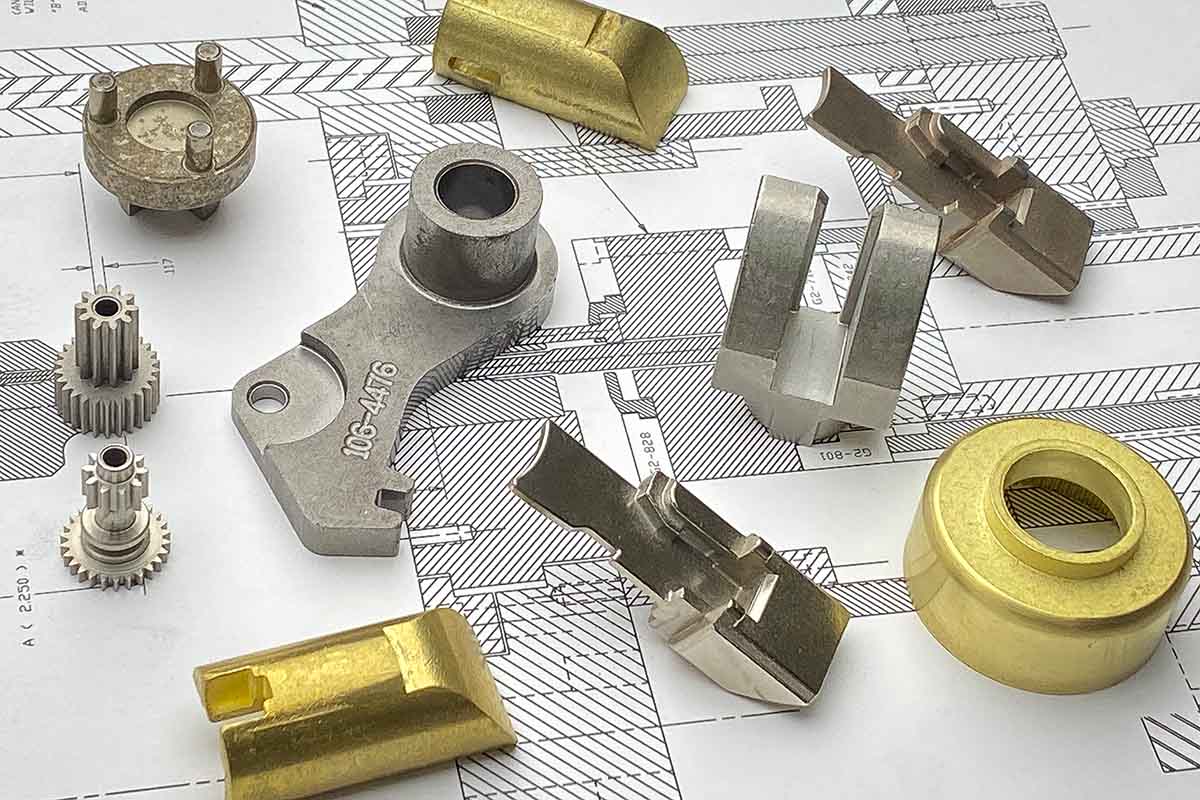
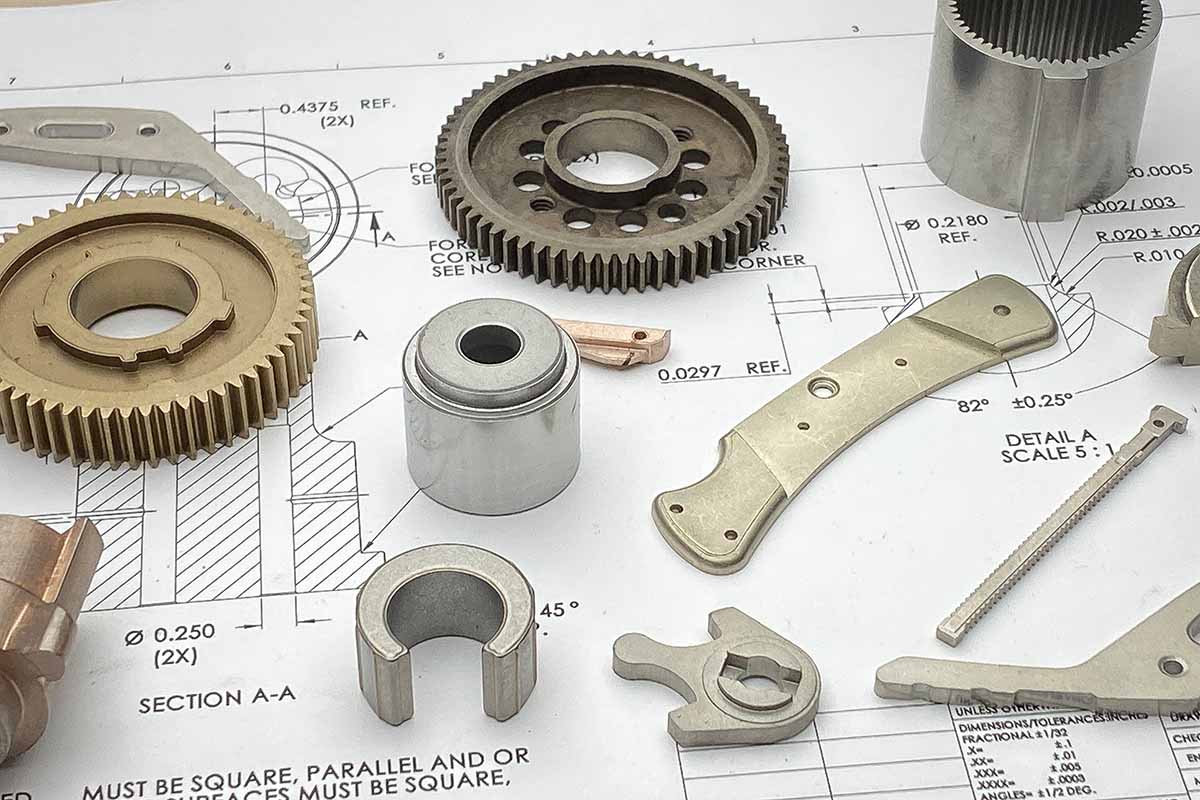
Economic mass production of precision parts
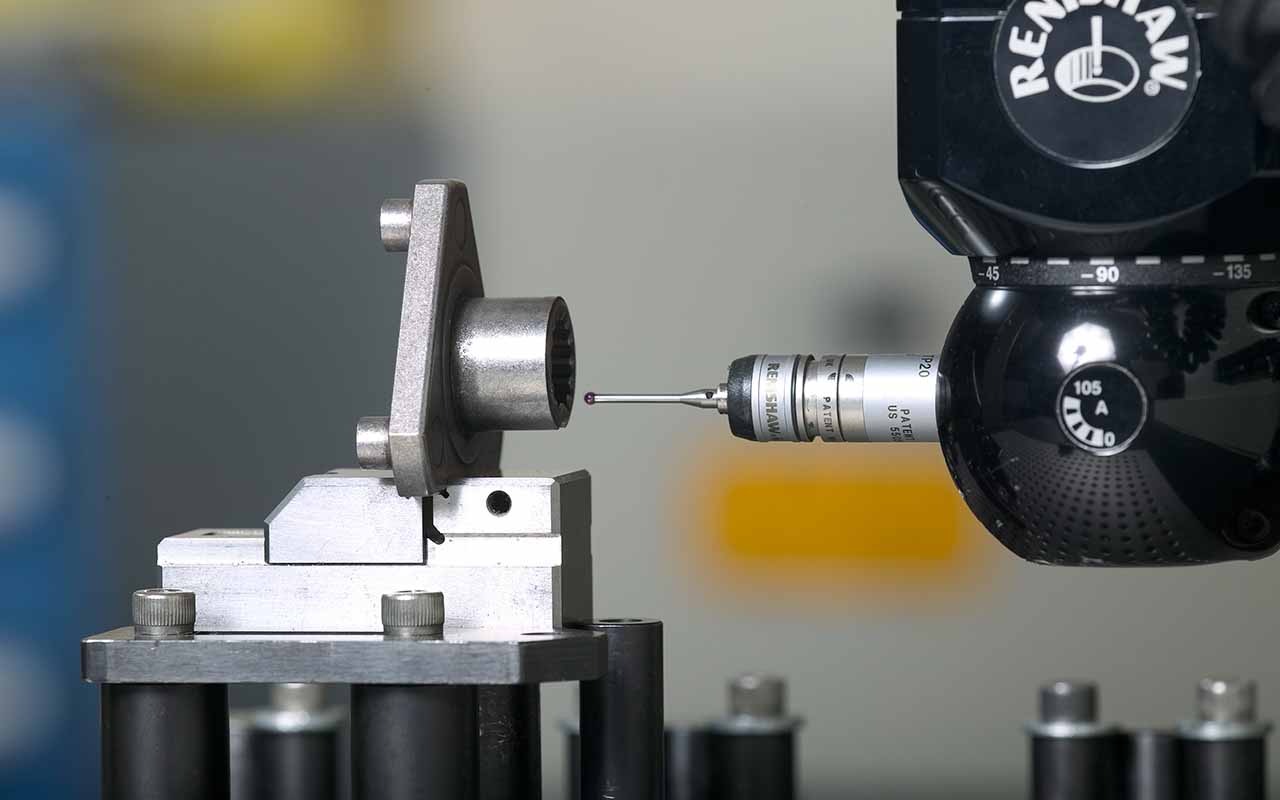
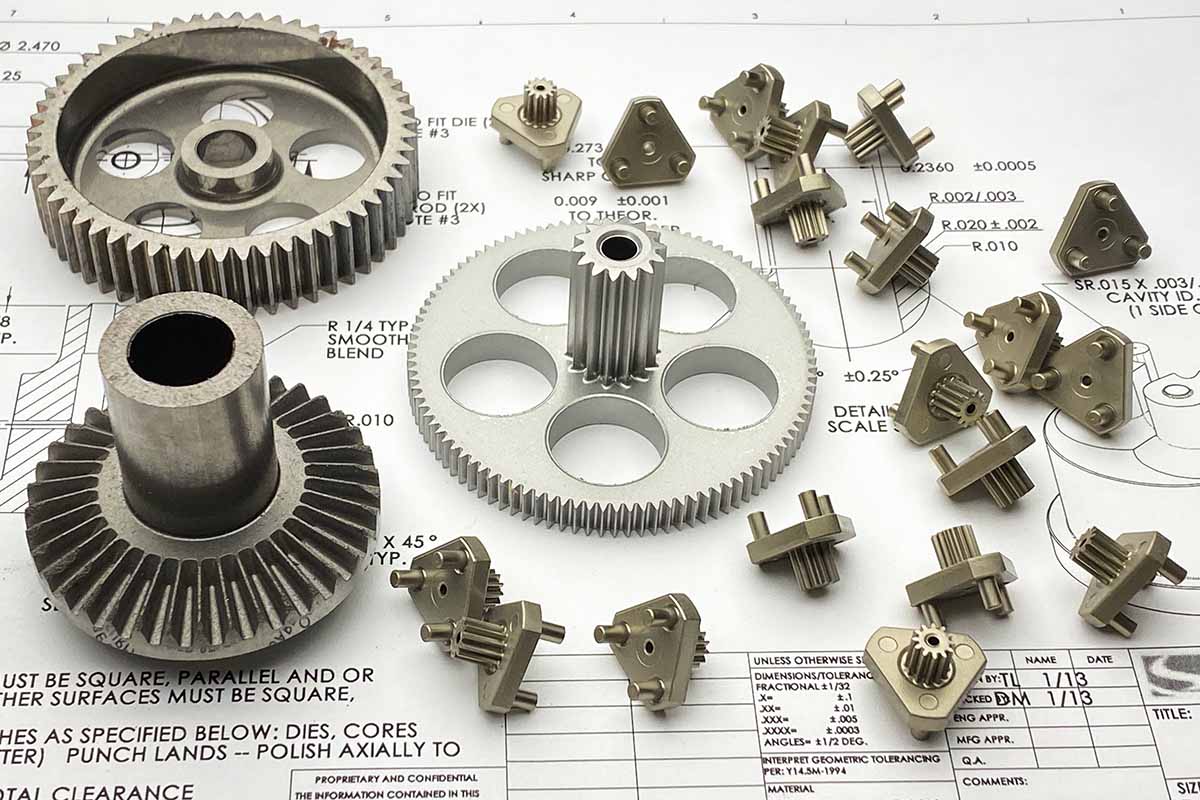
Powder metallurgy is a well-established mass production method for structural parts, bearings, filters, tool parts, magnets, friction materials, contact elements and components from refractory metals. Its basic steps are powder· production, mixing, molding into shapes, and sintering. Optional manufacturing steps like sizing, coining, repressing and resintering, forging, or metal infiltration may follow.
The unique advantages of the powder metallurgy process are:
- Saves production steps.
- Produces components with close tolerances which eliminate additional machining.
- Is versatile, a multitude of parts can be produced on identical production equipment by changing only the tooling.
- Produces complex shapes which would call for additional assembly or machining steps if alternative production techniques were used.
- Uses raw materials and energy most efficiently, as seen in Figure 1.
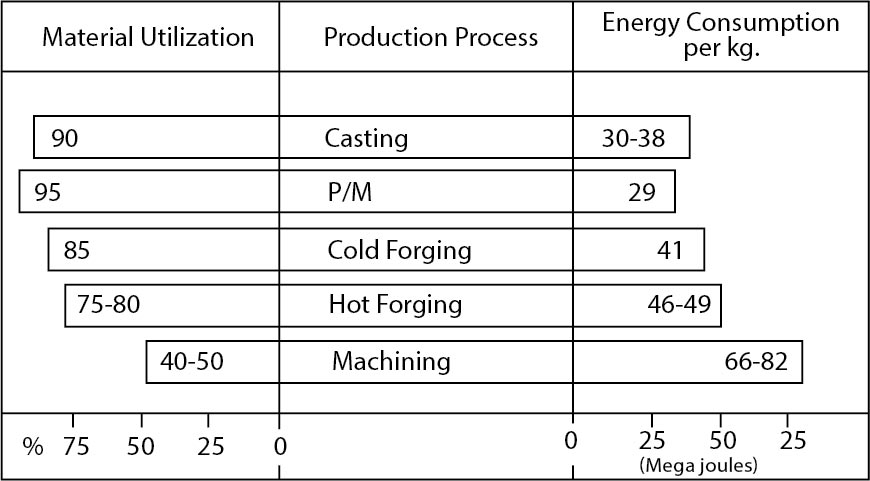
FIGURE 1
Material utilization and energy required to produce 1 kg. of finished component for different manufacturing techniques. The energy value includes amount of energy to produce the semifinished starting material from ore.