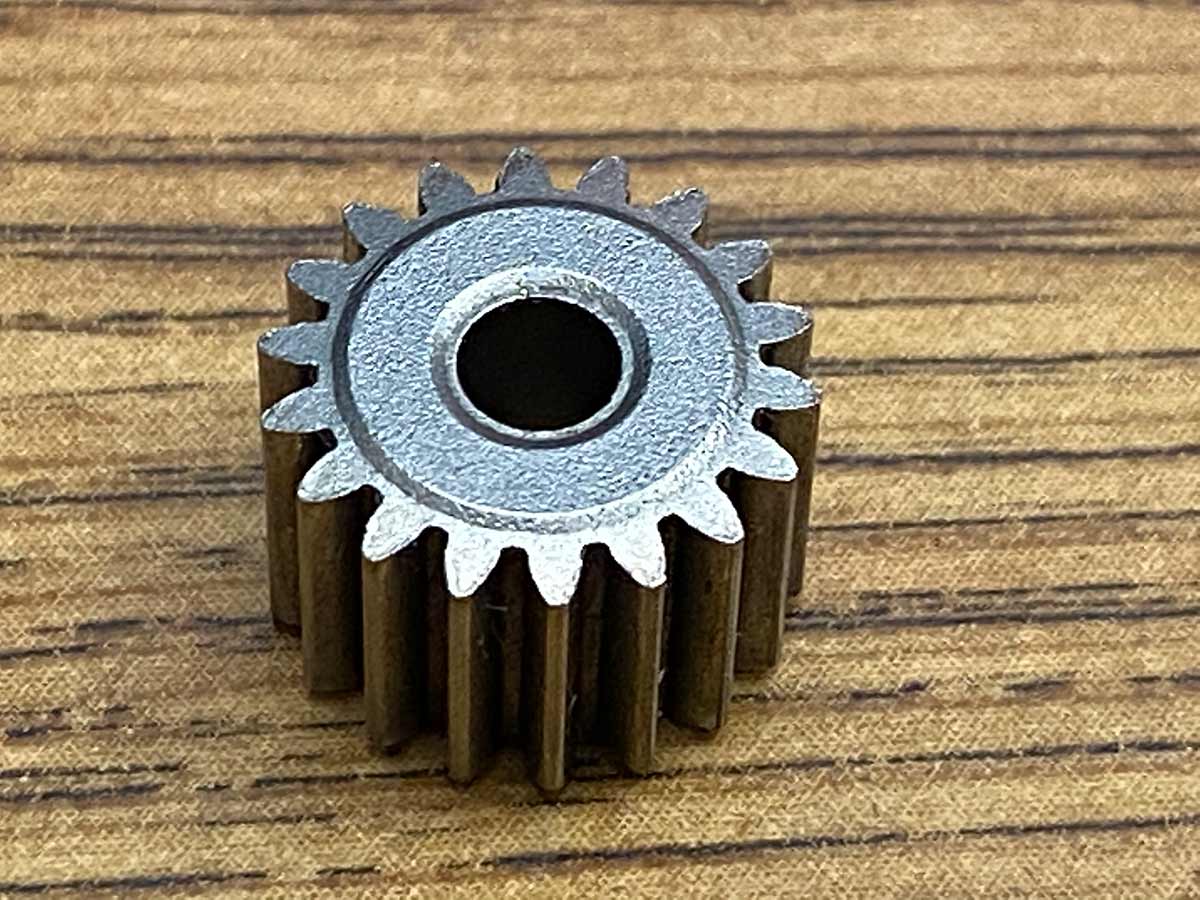
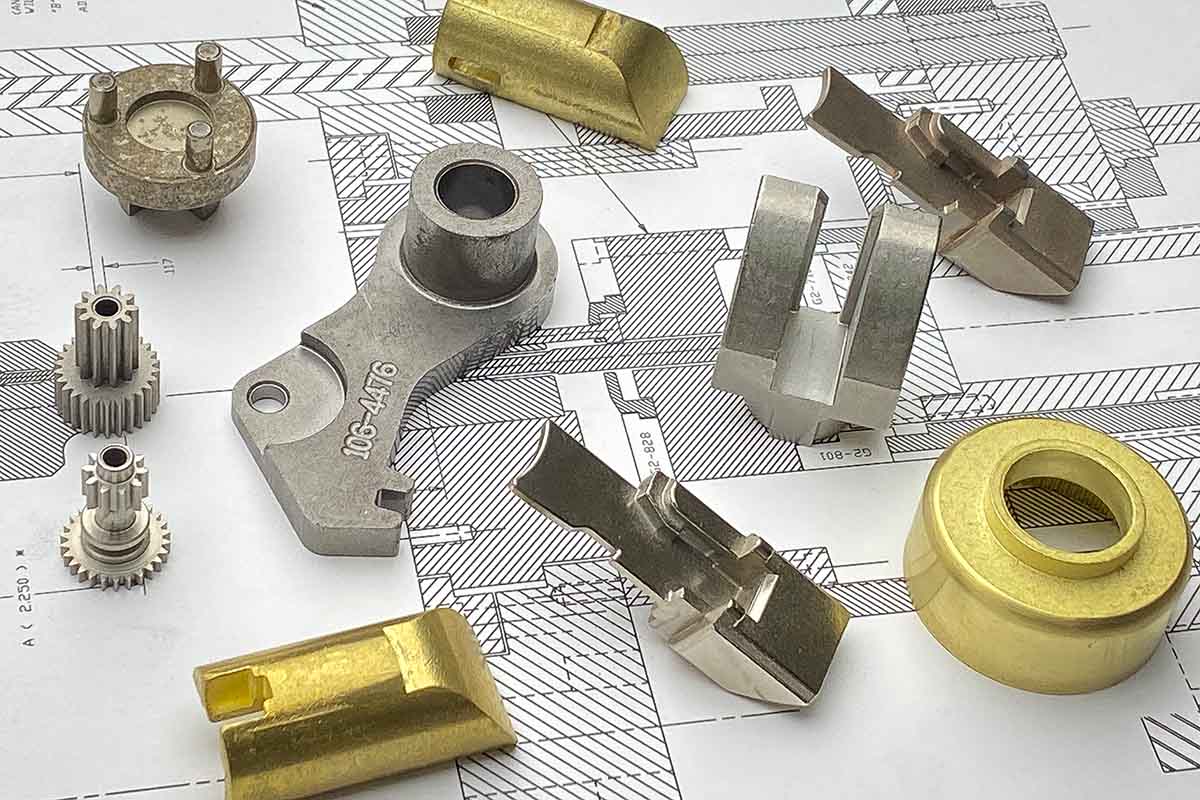
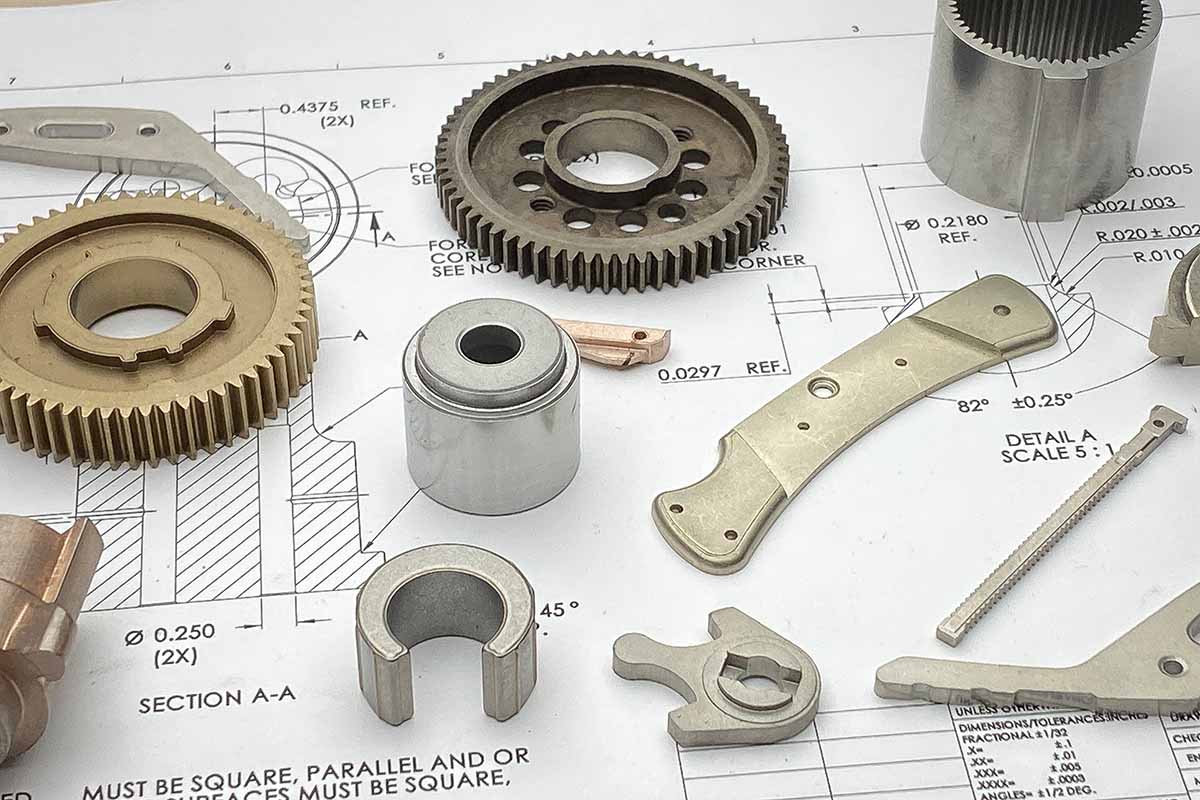
Main part made at ASCO Sintering are iron powdered metal parts
we would like to share some science behind the scenes:
Iron(Fe), a Block D element that is recognized by its atomic number 26, has a relative isotopic mass of 55.845, a melting point, and a boiling point of 1538 degrees Celsius and 2861 degrees Celsius respectively. It’s a metal found in group 8 of the periodic table and exists in the first transition series. Iron(Fe) is the fourth most common element on Earth’s crust by mass and most of Earth’s core is said to be iron.
Iron is hardly found in free elements as it tends to effortlessly oxidize, it normally exists in minerals/rocks that are considered as Iron ores, these minerals/ rocks are rich in metallic iron that can be economically extracted, the said minerals exist in the form of siderite, goethite, hematite or magnetite.
Iron Powdered Metal Parts main processes
The iron ores can be broken down to an iron powder through four main processes:
- Atomization
The process of atomization involves the production of iron powder by the use of either liquid or gas spray on molten metals. The metal steam is poured into jets of water /gas that makes it disintegrate. This process aims to atomize the molten metal into small particles that easily solidify before it gets into contact with each other and surfaces around them. This process is a significant method in the production of iron metal powder pieces.
- Solid-state reduction
The solid-state reduction process involves mixing iron ores with other materials, normally carbon. After mixing, the mixture is passed through a heater that generates a reaction that aims to decrease the carbon and oxygen amount in the powder. The metal mix is crushed and non-metal materials are removed.
Solid-state reduction is one of the old ways that can require about 3 days to fully decrease the iron ores to iron.
- Electrolysis
Electrolysis is a process that operates on an uninterrupted electric current to steer a non-spontaneous reaction. The process requires certain conditions to be effectual, these conditions include proper:-
- Temperature
- Density
- Electrolyte composition
When the conditions are met, electrolysis produces metal powders that are clean and dense. This process is expensive compared to other processes in the making of metal powder.
- Chemical
Chemical powder metallurgy is a process of acquiring metals from respective ores. The simplest chemical powder treatment includes the transfer of electrons between two elements. Involvement from solution, and thermolysis. The metal powder created can have a huge difference in properties and still have controlled particle dimensions and shapes. Powders that use oxide reduction are frequently characterized as “spongy” this is due to the presence of pores within them.
The product from this process can be used in the manufacturing of iron powdered metal parts through a process known as powder metallurgy. The powder metallurgy process has over the years proved to have loads of advantages over the competing metalworking technology, some of the advantages are:
- Reduced cost of production.
- It enhances a high production rate for complex parts
- It reduces scrap losses by the utilization of material of up to 97% of the initial material in the final parts.
- It makes a good exterior finish.
- It provides lasting performance reliability in an extensive application
- Facilitates the production of unique shapes that seem impractical with other processes.
- Materials made from powder metallurgy processes can be heat treated to escalate their strength or reduce wearing out.