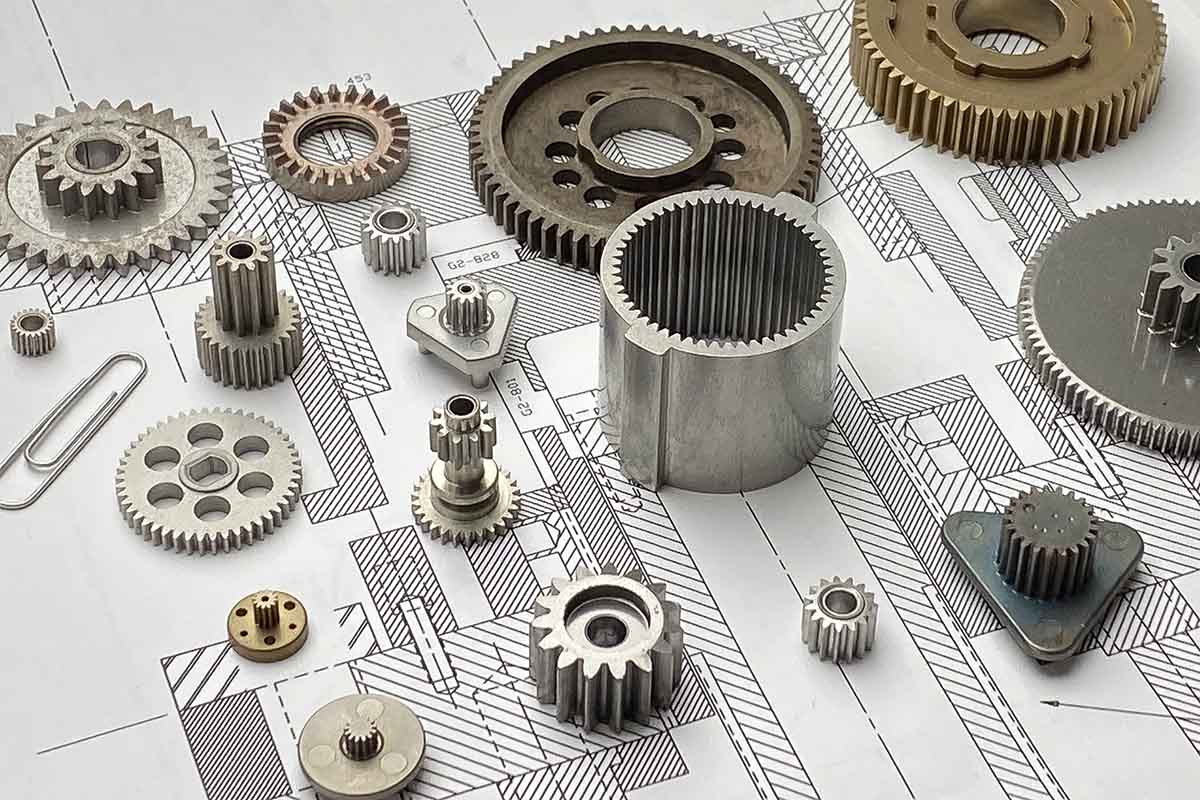
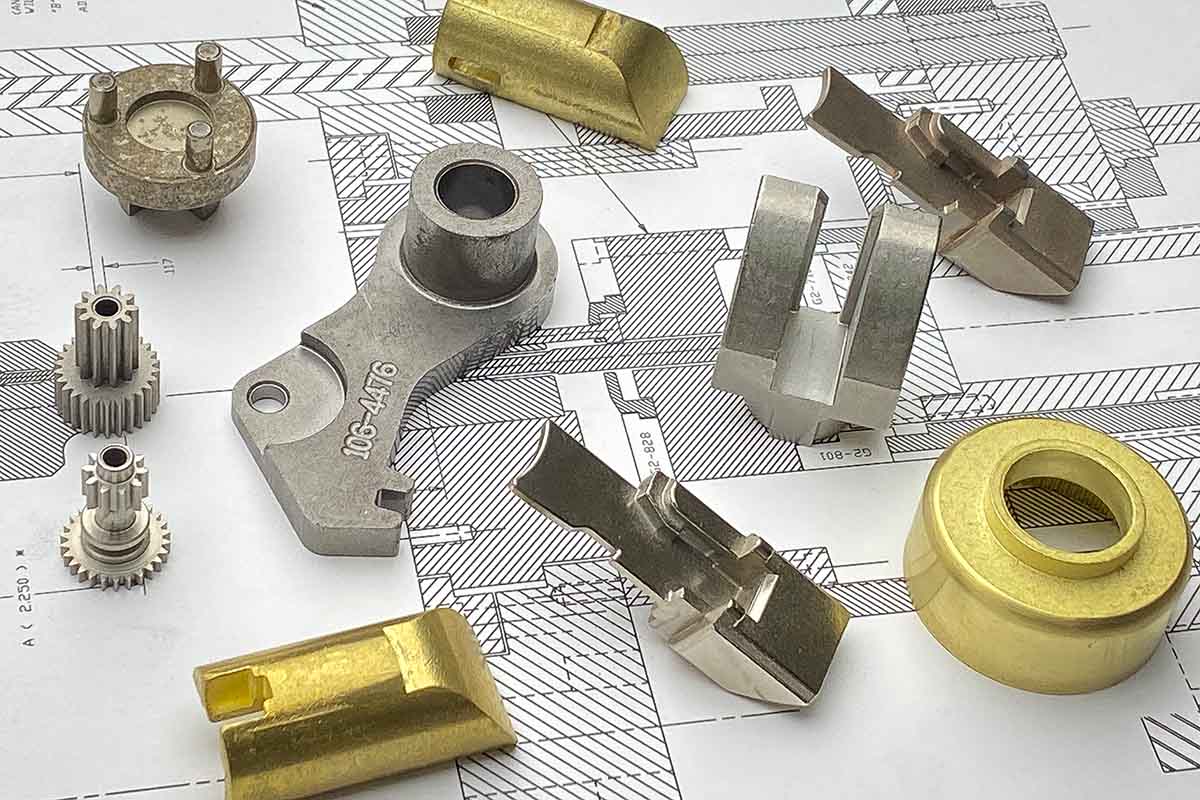
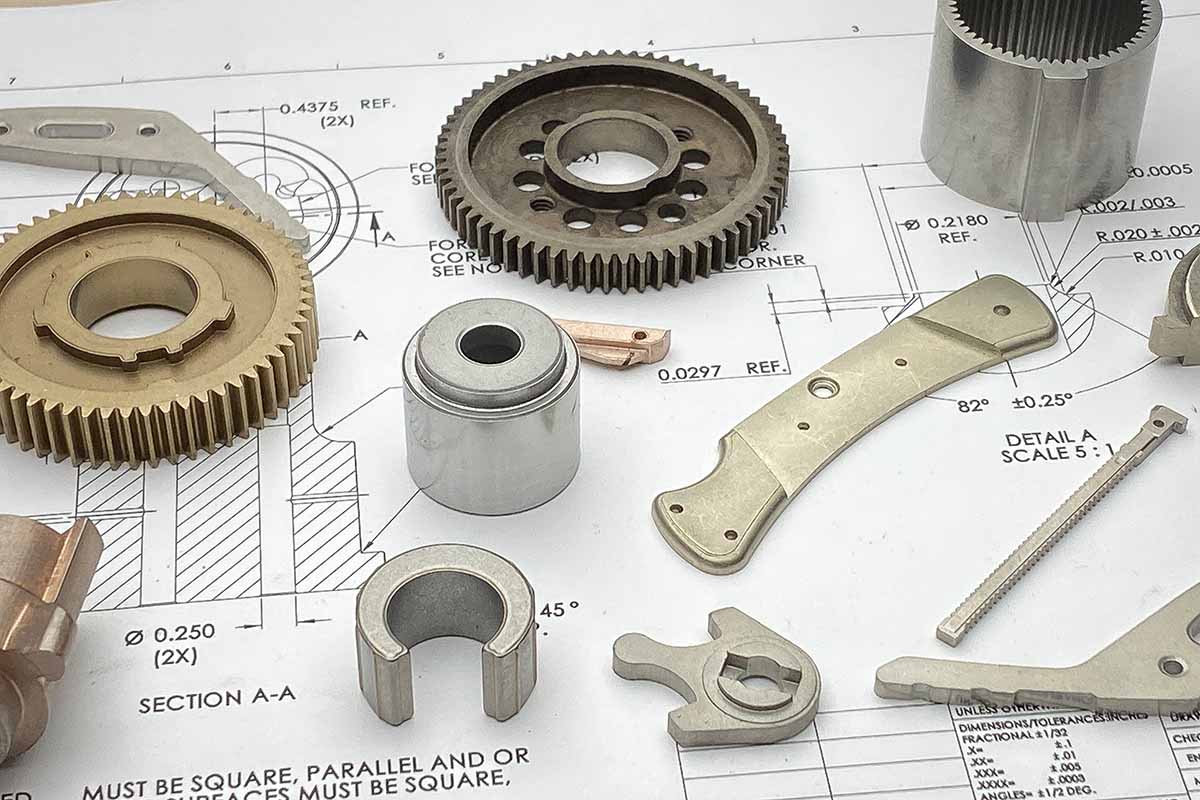
Gears are incredibly important for driving machines and other devices, and it’s critical to get the right type for the job. In this article, we’ll compare sintered vs machined gears, and explain the benefits of each.
First things first — What are sintered gears and machine gears?
Sintered Gears
Sintered gears are what most people think of when they hear the word “gear” — Sintered gears are made by the powdered metal (PM) method by following these steps:
- Mixing metal powders.
- Compacting the materials into the desired gear shape and size.
- Heating the compacted shape under controlled temperature and pressure.
Hence, metallurgical particles fuse together, which provides the gear with a lot of strength and durability.
Machined Gears
On the other hand, machined gears are made differently by cutting a gear shape with a machine. Common gear-cutting processes include:
- Hobbing
- Grinding
- Milling
For extreme precision and accuracy, some engineers prefer using CNC machining to manufacture gears.
Sintered vs Machined Gears
Here are some major differences between sintered vs machined gears:
Production Costs
Sintering is a non-contact molding process, which creates less production cost because no waste material during the manufacturing process. In other words, it’s cheaper than drilling or cutting — especially when you consider that with sintered metals production processes won’t need any additional oils or lubricants.
Time of Production
In general (for small orders), it takes a slightly more time to produce machined gears than sintered gears. Among gears with cutting processes, grinding may take a little longer because of polishing and finishing.
However, if the order is large, sintering is better than conventional gear machining as machined gears.
Quality of Sintered and Machined Gears
Comparing the hardness, strength, and durability, there’s no denial that sintered gears are way more powerful than machined gears.
Every industry has its own machining and automation requirements. Gears are a fundamental part of every industry. Therefore, every industry needs specific properties in its gears. To meet their standards, manufacturers can also use your favorite additives such as Nickel, Molybdenum, and Chromium to alter the properties of the gear.
On the other hand, manual machining cannot achieve quality standards. But, CNC machining does with advanced software and CNC machining guidelines.
Scrap Waste
While manufacturing machined gears, the process produces a large amount of scrap metal. In contrast, sintered gears manufacturing processes produce little to no waste as it uses a precision-controlled system.
Although machined gears scrap is recyclable, it still needs significant costs to recycle. Due to that, most machinists discard it.
Design Flexibility
Powder metallurgy is an “additive process,” which means that design starts from the ground up rather than by working on a slab of material. Therefore, it allows a geometrically complex design.
Powder metal allows you to design difficult geometries that would be impossible to create either by manual or CNC machining.
Sintered vs Machined Gears — Conclusion
Machined gears are a cheaper product in comparison to sintered gears. However, if you have greater needs or choose the best gear with more customized requirements at every scale of market production, then invest your money on ultra-precise sintered gears and high-quality additives in order not to regret it any later.